Trigeminal neuralgia is a pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, one of the most critical cranial nerves responsible for sensation in the face. Often referred to as the “suicide disease” due to the excruciating pain it causes, trigeminal neuralgia significantly impacts the quality of life for those affected.
Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by sudden, severe, stabbing or electric shock-like pain in the face. Pain episodes can last from a few seconds to several minutes, and occur in clusters, with long periods of remission in some cases. Over time, these episodes may become more frequent and intense.
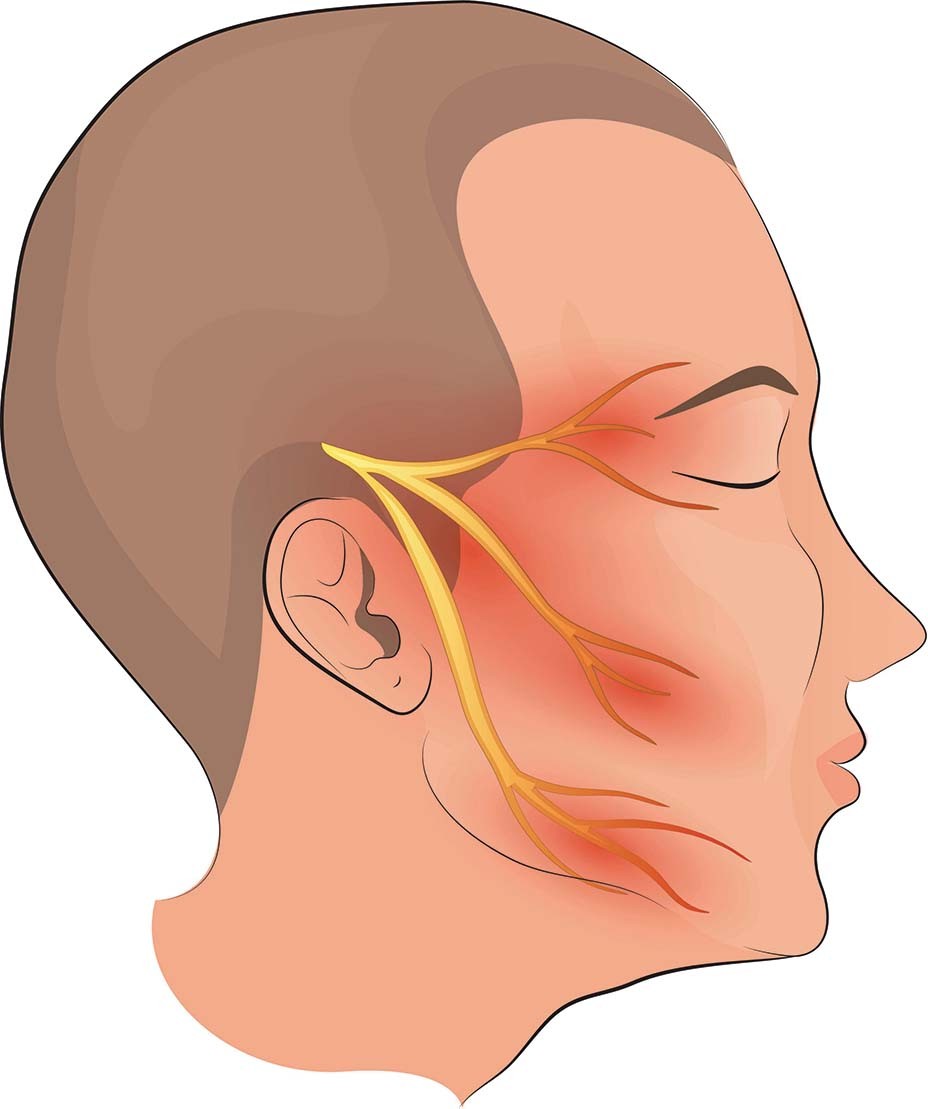
The various areas of face get sensation from a nerve – the trigeminal nerve. This nerve has three branches. One branch provides sensation to the upper face, including the forehead and eye. The other two branches cover the middle part of the face, including the cheeks, upper lip, and upper teeth and the lower jaw, lower teeth, and chin.
The hallmark symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is severe facial pain that is:
- Sharp and Intense: Often described as stabbing, electric shock-like, or burning.
- Triggered by Everyday Activities: Actions such as chewing, speaking, brushing teeth, or even a light breeze on the face can provoke pain episodes.
- Unilateral: The pain typically affects only one side of the face.
- Localized: The pain usually occurs in areas corresponding to one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Moreover, patients often live in fear of the next attack, as the pain is unpredictable and can severely limit daily activities.
Causes
The underlying cause of trigeminal neuralgia is related to irritation as well as compression of the trigeminal nerve. Common causes include:
- Blood Vessel Compression: The most common cause is a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve near its origin at the brainstem. This pressure damages the protective covering of the nerve, leading to abnormal pain signals.
- Multiple Sclerosis: In this disease, the myelin sheath is destroyed by the immune system, which can lead to trigeminal neuralgia as a secondary condition.
- Tumors: Rarely, a tumor pressing on the trigeminal nerve may cause symptoms.
- Injury or Trauma: Facial or dental trauma may irritate or damage the nerve.
- Unknown Causes: In some cases, there is no specific cause.
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to alleviate pain and improve quality of life. Options include:
Medications
- Anticonvulsants: Drugs such as carbamazepine and gabapentin are the first-line treatments for it. They work by stabilizing nerve activity.
- Muscle Relaxants: Baclofen in combination with anticonvulsants control the pain.
- Antidepressants: Doctors may prescribe them for patients with overlapping neuropathic pain conditions.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Microvascular Decompression: A surgical procedure where the blood vessel compressing the nerve is relocated or removed. This offers long-term relief for many patients.
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: A non-invasive option that uses focused radiation to damage the trigeminal nerve, reducing pain signals.
- Percutaneous Procedures: Techniques such as glycerol injections, balloon compression, or radiofrequency ablation are used to selectively damage nerve fibers to block pain signals.
- Acupuncture: It may provide relief for some patients.
Lifestyle Modifications
Patients can avoid triggers by making adjustments such as eating soft foods, using lukewarm water for facial washing, and avoiding cold weather.
Trigeminal neuralgia is not just a physical condition but also a psychological burden. The unpredictability and intensity of pain can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Therefore, building a strong support system and seeking counseling or therapy can help manage the emotional toll of the condition.
Read our full disclaimer.