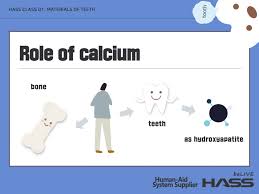
Calcium deficiency can significantly impact dental health because calcium is a main building block for teeth, just as it is for bones. Its deficiency weakens your teeth and jawbone, increasing decay, sensitivity and risk of permanent tooth loss.
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in your body. It contains about 96% mineral, mostly crystalline calcium, the hydroxyapatite. Low calcium levels can lead to softer, thinner enamel, making teeth more prone to tooth decay. It subsequently converts into cavities. This is because of less resistance to acid attacks from acid producing bacteria in your moth. The thinner enamel also exposes dentin, causing pain with hot/cold foods. The dentin is the sensitive layer under the enamel.
Calcium deficiency weakens bones because calcium is essential for bone strength and density. When the body lacks enough calcium, it starts using calcium stored in bones, making them fragile. Over the period of time, this can lead to osteopenia (early bone loss) and progress to osteoporosis, where bones become brittle and prone to fractures.These bone issues can cause Jawbone loss leading to loosen teeth, increasing gum recession and tooth loss.
Kids with calcium deficiency may suffer from delayed tooth development. They may have weak or discolored baby teeth. If the deficiency persists, their adult teeth may be poorly formed.
Signs of Calcium Deficiency in Teeth
Despite having good oral hygiene, more cavities than usual
Loosened teeth
Receding gums
Chipped, cracked or translucent teeth
How to Protect Your Teeth from Calcium Deficiency
- Eat Calcium-Rich Foods:
- Dairy:cow’smilk, cheese, yogurt.
- Leafy greens: Brocilli, Spinach
- Sea food: Sardines, Tofu, Scallop, Prawn
- Dry Fruits: Almonds, Walnut, Pistachios, Cashews, Dried apricot
- Get Enough Vitamin Das it helps absorb calcium. You can have it from sunlight, fatty fish, fortified foods.
- Consider Supplements if diet isn’t enough, but consult a doctor first.
- Avoid excess caffeine, soda and high-salt diets as they can leach calcium from bones
If you notice frequent cavities or brittle teeth, ask your dentist or doctor about checking calcium levels in you blood. For healthy teeth, jawbone, and gums, the normal calcium level should be maintained within the range of 8.5 – 10.5 mg/dL. This level ensures proper mineralization of teeth, strength of the jawbone, and stability of gum tissues. Both low calcium (hypocalcemia) and high calcium (hypercalcemia) can negatively affect oral and overall health. Adequate vitamin D and phosphorus are also vital for calcium absorption and bone health.
Read our full disclaimer.