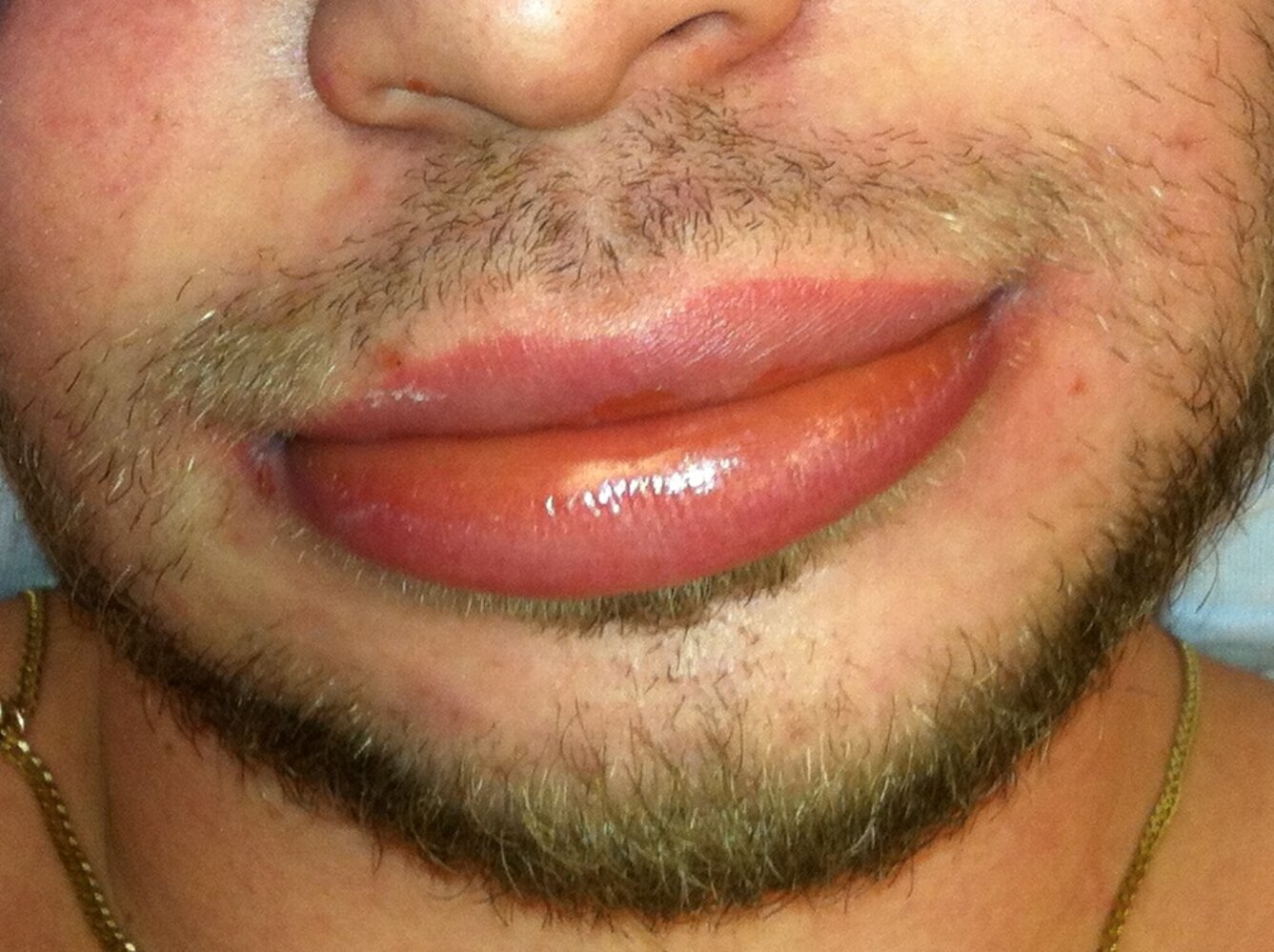
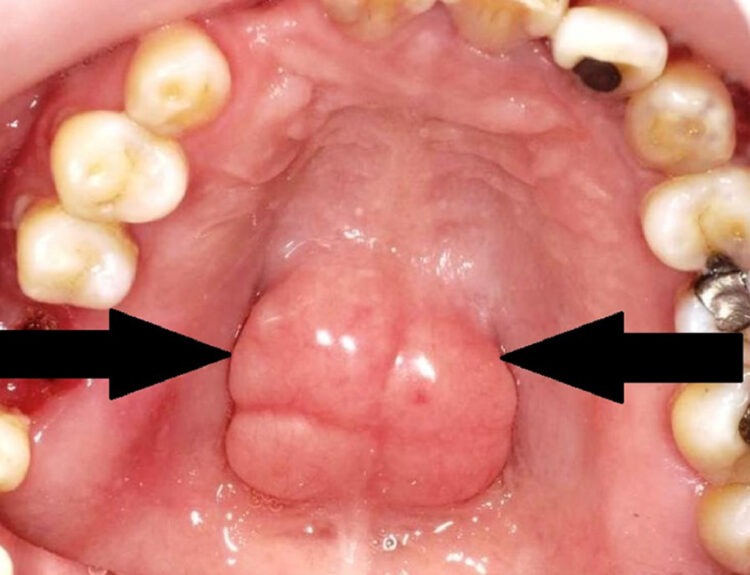
Angioedema is an allergic reaction that results in swelling inside the mouth. There are various reasons for angioedema to occur;
Causes:
Food Allergies: Common culprits include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy products.
Medicines: Certain medicines, such as antibiotics (e.g., penicillin), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and blood pressure medications (e.g., ACE inhibitors), can cause allergic reactions.
Insect Stings or Bites: Bee stings, wasp stings, and other insect bites can trigger allergic reactions.
Environmental Allergens: Pollen, mold, pet dander, and dust mites can sometimes cause oral swelling.
Latex: Allergic reactions to latex can cause swelling in the mouth, especially if latex products come into contact with the oral mucosa.
Oral Care Products: Some people may react to ingredients in toothpaste, mouthwash, or dental materials.
Hereditary angioedema: This is a rare genetic condition that causes recurrent episodes of angioedema.
Idiopathic: In some cases, the cause of angioedema is unknown.
Symptoms:
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, cheeks, or throat
- Itching or tingling sensation in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- In severe cases, difficulty breathing (which is a medical emergency)
Prevention:
Avoid known triggers: If you know what triggers your angioedema, avoid those substances or situations.
Allergy Testing: If you frequently experience allergic reactions, consider seeing an allergist for testing to identify specific allergens.
Carry Medications: If you have a known severe allergy, always carry an epinephrine auto-injector and antihistamines.
Read Labels: Be vigilant about reading food labels and asking about ingredients when eating out.
Inform Healthcare Providers: Make sure your healthcare providers are aware of any known allergies before prescribing medications or performing dental procedures.
.
Treatment:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine, cetirizine) can help reduce mild allergic reactions and swelling.
- Epinephrine: For severe reactions (anaphylaxis), an epinephrine injection (EpiPen) is the first-line treatment. This is a medical emergency, requring immediate medical attention.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injectable corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Emergency Care: If there is significant swelling that affects breathing, seek emergency medical care immediately. This may involve additional treatments such as oxygen therapy or intravenous (IV) medications.
- Topical Treatments: In some cases, topical antihistamines or corticosteroids may be used to alleviate symptoms.
Read our full disclaimer.