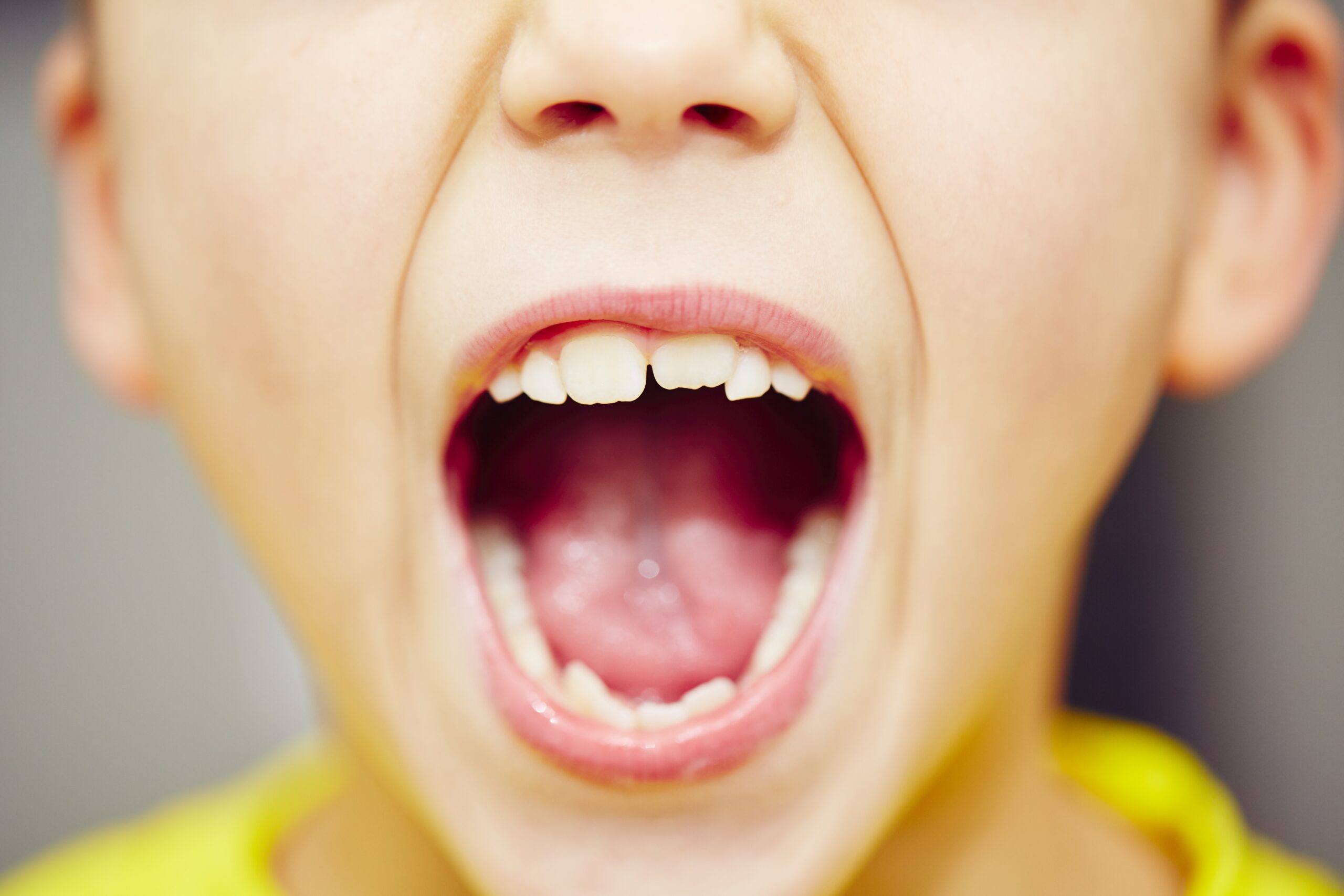
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, is a common condition among children, affecting approximately 3 out of 10 kids. While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors contribute to this habit. One prominent reason is dental misalignment; children whose upper and lower teeth do not fit together properly often grind their teeth unconsciously. Kids experiencing physical discomfort, such as earaches, stomachaches, toothaches, or other bodily pains, may grind their teeth as a coping mechanism to relieve their discomfort.
Children with neurological conditions like cerebral palsy are also more prone to bruxism. Another contributing factor is long-term medication use, as certain drugs may trigger teeth grinding as a side effect. In older children, psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or school-related pressures can lead to this habit.
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in minerals like calcium and magnesium, may also play a role in teeth grinding. Moreover, parasitic infections, such as intestinal worms, can contribute to bruxism. These parasites release toxins that irritate the nervous system, leading to involuntary teeth grinding.
When a child grinds his/her teeth due to intestinal worms, the primary solution is administering anti-worm medication. Doctors often recommend deworming medicines for affected children, as eliminating the parasites can stop the grinding habit.
Intestinal worms, such as pinworms (threadworms), roundworms, or tapeworms, release toxins that irritate the nervous system. This irritation leads to involuntary teeth grinding, especially during sleep. Moreover, worms disrupt nutrient absorption, potentially causing deficiencies in minerals like calcium and magnesium, which are linked to muscle function and may worsen bruxism.
Sign & symptoms
- Itching around the anus (especially at night, when female pinworms lay eggs)
- Restless sleep or frequent waking
- Stomach pain, nausea, or loss of appetite
- Visible worms in stool or near the anal area
Deworming Treatment
If worms are confirmed (through stool tests or visible signs), pediatricians typically prescribe anti-worm medications. These medications paralyze or kill the parasites, allowing the body to expel them naturally. A second dose may be needed after 2 weeks to ensure all worms and newly hatched eggs are eliminated.
Preventive Measures for Parents
To prevent reinfection, parents should:
- Maintain hygiene (frequent handwashing, keeping nails short)
- Wash bedding and underwear in hot water
- Avoid scratching the anal area (to prevent egg transfer)
- Ensure clean food and water to avoid contamination
When to See a doctor
If teeth grinding persists even after deworming, doctor may prescribe further evaluation to check for other causes like dental misalignment, stress, or nutritional deficiencies.
Read our full disclaimer.