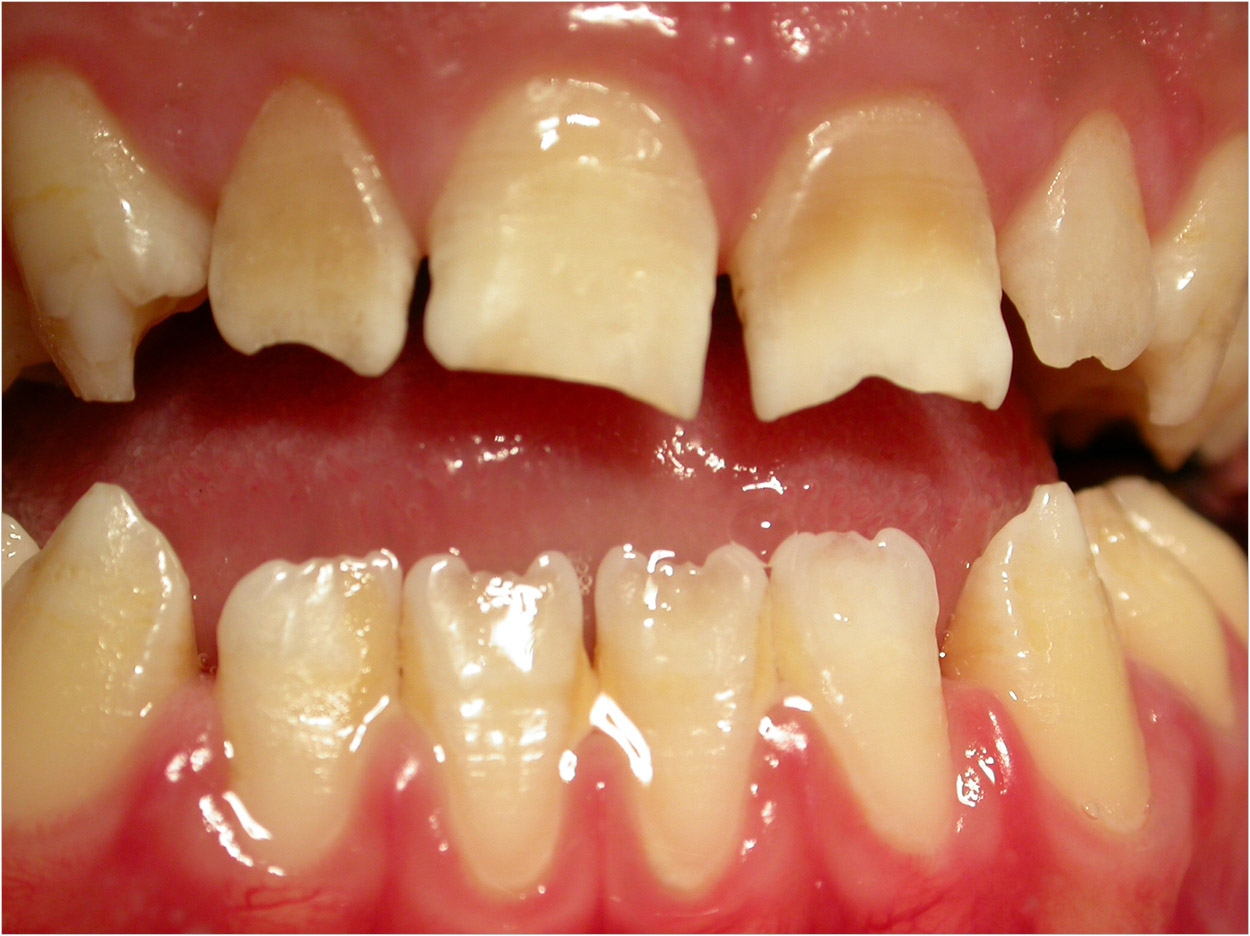
The appearance of teeth plays a crucial role in a person’s overall facial aesthetics and self-confidence. While beauty is subjective, some dental conditions contribute to what is commonly perceived as “ugly-looking teeth.” Various factors can affect the appearance of teeth. T
- Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the shape, size, alignment, and color of teeth. Some individuals inherit irregularly shaped teeth. Congenital conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta or dentinogenesis imperfecta can cause teeth to appear discolored or malformed.
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate oral care is one of the most common causes of unattractive teeth. Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque and tartar to build up, leading to discoloration and gum disease. Neglecting oral hygiene also increases the risk of cavities, which can create dark spots, decay, and tooth loss, all of which contribute to an unappealing smile.
- Dietary Habits
The foods and beverages we consume can significantly impact the appearance of teeth. Sugary and acidic foods contribute to enamel erosion and cavities, making teeth look decayed and unattractive. Dark-colored beverages such as coffee, tea, red wine, and soda can stain teeth over time, resulting in a brownish tint.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco products contain chemicals that stain teeth, turning them yellow or brown. Smoking also increases the risk of gum disease, which can lead to gum recession and tooth loss. Moreover, tobacco use reduces saliva production, making it easier for plaque and bacteria to accumulate on teeth.
- Tooth Injuries
Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause chipped, cracked, or broken teeth. These damages can make teeth appear uneven and unattractive. In severe cases, trauma can lead to tooth loss, which may create gaps in the smile and negatively affect facial symmetry.
- Crooked Teeth
Crooked, overcrowded, or widely spaced teeth can significantly impact a person’s smile. Malocclusion occurs due to genetic factors, thumb-sucking habits in childhood, or the early loss of baby teeth. Uneven teeth can also create difficulties in maintaining oral hygiene, leading to further discoloration and decay.
- Medications and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as tetracycline antibiotics taken during childhood, can cause permanent tooth discoloration. Other medical conditions, such as acid reflux (which exposes teeth to stomach acids) and diabetes can negatively affect dental aesthetics
- Excessive Fluoride Exposure
Fluoride is widely used in dentistry to prevent tooth decay, but excessive exposure can have adverse effects on teeth making them look ugly.
Dental Fluorosis: Overexposure to fluoride during tooth development before the age of 8 causes Fluorosis. White streaks, brown stains, pitting, and surface irregularities appear on the enamel.
Enamel Hypomineralization: High fluoride intake interferes with proper enamel mineralization. Weakened enamel, leading to increased porosity and potential structural defects become visible.
Delayed Tooth Eruption: Fluoride can slow down enamel formation, potentially delaying tooth eruption and affecting normal dental development.
- Aging and Natural Wear
As people age, their teeth naturally undergo wear and tear. Enamel gradually wears down, exposing the yellowish dentin underneath. Moreover, years of consuming staining foods and beverages, as well as changes in saliva production, can contribute to a dull, discolored appearance.
Treatment Options
If you are concerned about the appearance of your teeth, it is important to see a dentist. A dentist can help you identify the cause of your problem and recommend treatment options.
- Teeth whitening: Teeth whitening can remove stains from teeth and make them look brighter.
- Dental veneers: Dental veneers are thin shells of porcelain that are bonded to the front of teeth to improve their appearance.
- Dental crowns: Dental crowns are caps that cover the entire tooth to improve its appearance and function.
- Dental implants: Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are placed in the jawbone to support a replacement tooth.
- Orthodontics Braces: Orthodontics, such as braces or Invisalign, can straighten crooked teeth.
Read our full disclaimer.