Joint pain is Arthritis and gum disease is Periodontitis. Both are common chronic conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. While they may seem unrelated at first glance, emerging research highlights a significant link between the two diseases. Understanding the connection is essential for improving health outcomes and providing comprehensive care to affected individuals.
Arthritis:
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing different conditions characterized by joint inflammation, pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. The most prevalent forms of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disorder, and osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear of joint cartilage. Rheumatoid arthritis, in particular, has been closely associated with systemic inflammation and immune system dysfunction.
Periodontitis:
Periodontal diseases are chronic inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues supporting the teeth. They range from mild gingivitis, characterized by gum redness and swelling, to more severe periodontitis, which leads to gum recession, bone destruction. It eventually causes tooth loss. Periodontal diseases are primarily caused by bacterial plaque, but genetic, environmental, and systemic health factors contribute to their development as well.
Connection between Arthritis & Periodontitis:
The primary link between arthritis and gum diseases lies in their shared inflammatory mechanisms. Both conditions are driven by chronic inflammation, which is the body response to harmful stimuli such as bacteria or an overactive immune system. In rheumatoid arthritis, the defense system mistakenly attacks joint tissues, leading to persistent inflammation. Similarly, Periodontitis occurs when the body defense system overreacts to bacteria around the teeth. This overreaction causes inflammation, which damages the tissues and bone that support the teeth.
Research Studies have shown that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop periodontal disease, and vice versa. Both conditions involve inflammation. Increased levels of certain chemicals in the body cause this inflammation.. These chemicals are cytokines, such as TNF-α and interleukins (IL-1, IL-6) which signifiantly damage tissues and keep the inflammation progressing.
Role of Mouth Bacteria:
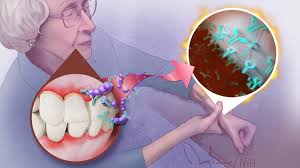
The oral bacteria play a role in the link between arthritis and gum diseases significantly. Some types of gums bacteria in the mouth, like Porphyromonas gingivalis, can worsen rheumatoid arthritis. The bacteria make an enzyme called PAD that changes proteins in the body. In some people, this change causes the body to mistakenly attack its own tissues, leading to rheumatoid arthritis.
Impact on Quality of Life
Both arthritis and gum diseases significantly impact quality of life, particularly when they coexist. Chronic pain, difficulty in performing daily activities, and emotional distress are common among individuals with arthritis. Similarly, periodontal disease can lead to discomfort, difficulty eating, and social embarrassment due to bad breath or tooth loss. The combination of these conditions can compound physical and psychological burdens.
Management and Prevention
Addressing the link between arthritis and gum diseases requires an integrated approach to care. For individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, regular dental check-ups and rigorous oral hygiene practices are necessary to prevent periodontal disease. Similarly, periodontal therapy may help reduce systemic inflammation and improve arthritis symptoms. Moreover, lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet, smoking cessation, and stress management, benefit both conditions by reducing inflammation.
Read our full disclaimer.