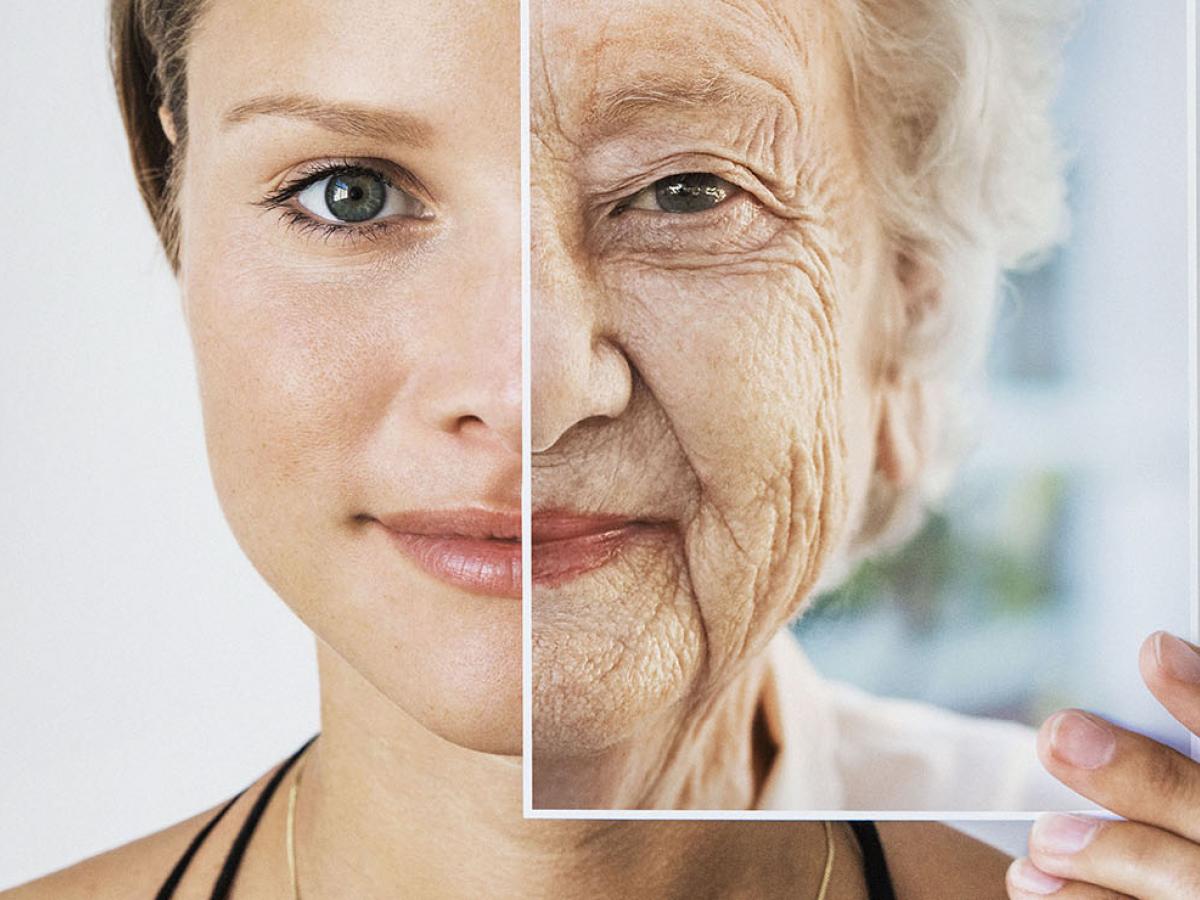
Aging is an inevitable process that affects every living being. As we grow older, our body undergoes various physiological, structural, and functional changes. While aging is a natural part of life, understanding its impact on the body can help us adopt healthier habits to promote longevity and well-being.
Muscle and Bone Decline: One of the most noticeable effects of aging is a decline in muscle mass and bone density. This condition, known as sarcopenia, leads to reduced strength and mobility, making older individuals more prone to falls and fractures. Osteoporosis, a common age-related bone disorder, results in brittle and weak bones due to decreased calcium absorption. Regular weight-bearing exercises and a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help slow down these changes.
Impact of Aging on Heart: With age, the heart and blood vessels also undergo significant changes. Arteries become stiffer due to the loss of elasticity, leading to higher blood pressure and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The heart may have to work harder to pump blood efficiently, contributing to conditions such as hypertension and heart disease. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Aging Brain and Nervous System: Aging affects the brain and nervous system, leading to slower cognitive function and memory decline. While minor forgetfulness is common, conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease can severely impact cognitive abilities. Engaging in mental activities, such as reading, puzzles, and learning new skills, can help keep the brain active and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
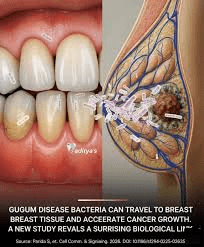
Effect on Oral Health: Aging has a significant impact on dental health. Over time, enamel wears down, making teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity. Gum recession can expose tooth roots, leading to discomfort and an increased risk of cavities. Dry mouth (xerostomia) is also common due to reduced saliva production, which can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease. Bone loss in the jaw can result in loose or missing teeth. Regular dental checkups, good oral hygiene, and staying hydrated can help maintain oral health as one ages.
Deterioration of Digestion and Gut Health: The digestive system also experiences changes with age. Reduced saliva production, slower metabolism, and weakened digestive muscles can lead to issues such as constipation and indigestion. A fiber-rich diet, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity can support a healthy digestive system
Aging Immune system: As we age, the immune system weakens, making the body more susceptible to infections, diseases, and slower wound healing. Vaccinations, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help boost immunity and protect against illnesses.
Impact on hair and skin: Aging also affects the skin and hair. The skin loses its elasticity and becomes thinner, leading to wrinkles and sagging. Hair follicles produce less melanin, resulting in graying hair. Proper skincare, hydration, and sun protection can help slow down visible signs of aging.
Recommended Strategies: While aging is inevitable, adopting healthy lifestyle choices can significantly improve quality of life in later years.
Engaging in physical activities such as walking, yoga, and strength training helps maintain muscle mass, bone strength, and overall mobility. Quality sleep is essential for cellular repair, memory consolidation, and overall well-being. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports overall health and slows down the aging process. Reading, socializing, and learning new skills can help maintain cognitive function and emotional well-being. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can reduce the negative impact of stress on the body.
.
Read our full disclaimer.