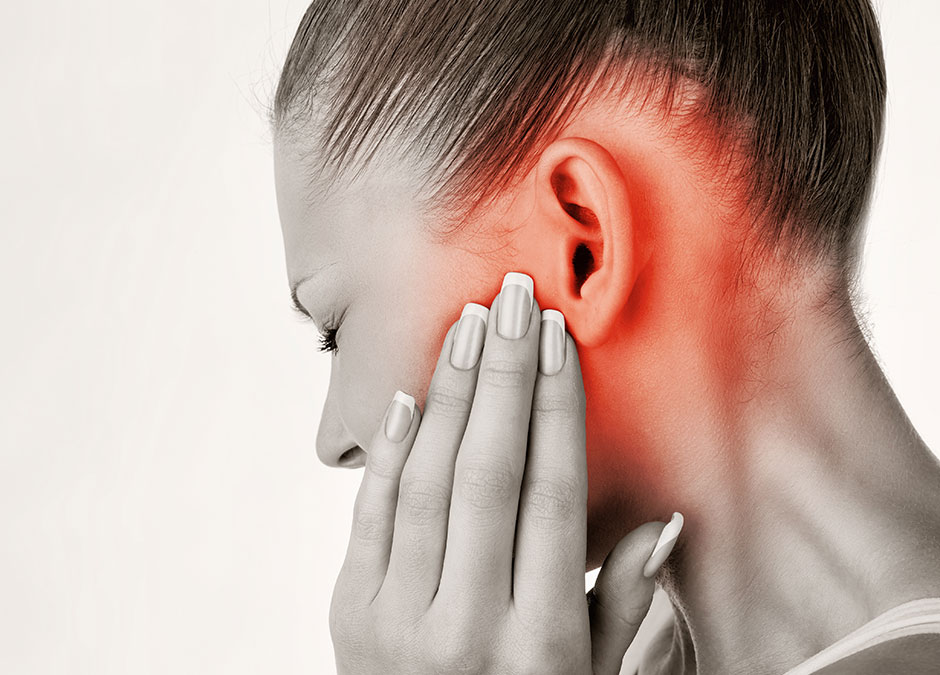
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction refers to a disorder affecting the joint that connects lower jaw (mandible) to your skull. This joint, located just in front of ears, enables jaw movements during chewing, speaking, and yawning. Besides clinical examination, for its diagnosis, dentists advise X-rays, CT scan, or MRI to get a detailed look at the joint structure.
Causes of Temporomandibuar joint dysfunction
- Teeth Grinding or Clenching: Puts extra pressure on the joint consequently causing pain
- Stress: Can lead to tight facial and jaw muscles, hence persistent discomfort
- Jaw Injury: Trauma to the jaw or surrounding muscles.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis in the TMJ.
- Misaligned Bite: Improper alignment of teeth can strain the joint.
- Habits: Even though chewing gum frequently, biting nails, or resting the chin on the hand appear innocent habits, they can cause TMJ dysfunction.
Symptoms:
- Jaw Pain or Tenderness: Pain near the joint, face, or around the ear.
- Difficulty or Pain While Chewing: Discomfort during eating or jaw stiffness.
- Jaw Clicking or Popping: A clicking or popping sound when opening or closing your mouth.
- Limited Jaw Movement: Difficulty in fully opening or closing the mouth.
- Headaches or Ear Pain: TMJ issues can mimic ear infections or cause tension headaches.
- Locking of the Jaw: The jaw may temporarily get “stuck” in an open or closed position, hence crestes panic
Management and Treatment:
Self-Care:
Apply warm or cold compresses to reduce pain or swelling.
Eat soft foods to minimize strain on the jaw.
Practice relaxation exercises or stress management techniques.
Dental Splints or Night Guards:
Dentists make Night Guards to wear to reduce grinding/clenching and relieve pressure on the TMJ. Moreover, they prescribe Anti-inflammatory pills, muscle relaxants, or pain relievers.
Physio Therapy:
A physiotherapist plays a significant role in alleviating temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction by using non-invasive techniques to reduce pain, improve joint function, and restore normal jaw movement. He/she recommends jaw exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint mobility. Besides this, using modalities like ultrasound, heat, cold therapy, or TENS can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Advanced Treatments (in severe cases):
Corticosteroid injections, arthroscopy, or surgery (rare).
How to Prevent TMJ Dysfunction:
- Avoid excessive gum chewing.
- Be mindful of your posture—keep your head aligned over your spine.
- Address teeth grinding or clenching early, especially during stressful periods.
- Regular dental check-ups to maintain proper bite alignment.
Read our full disclaimer.